Chevron Ruling Overview
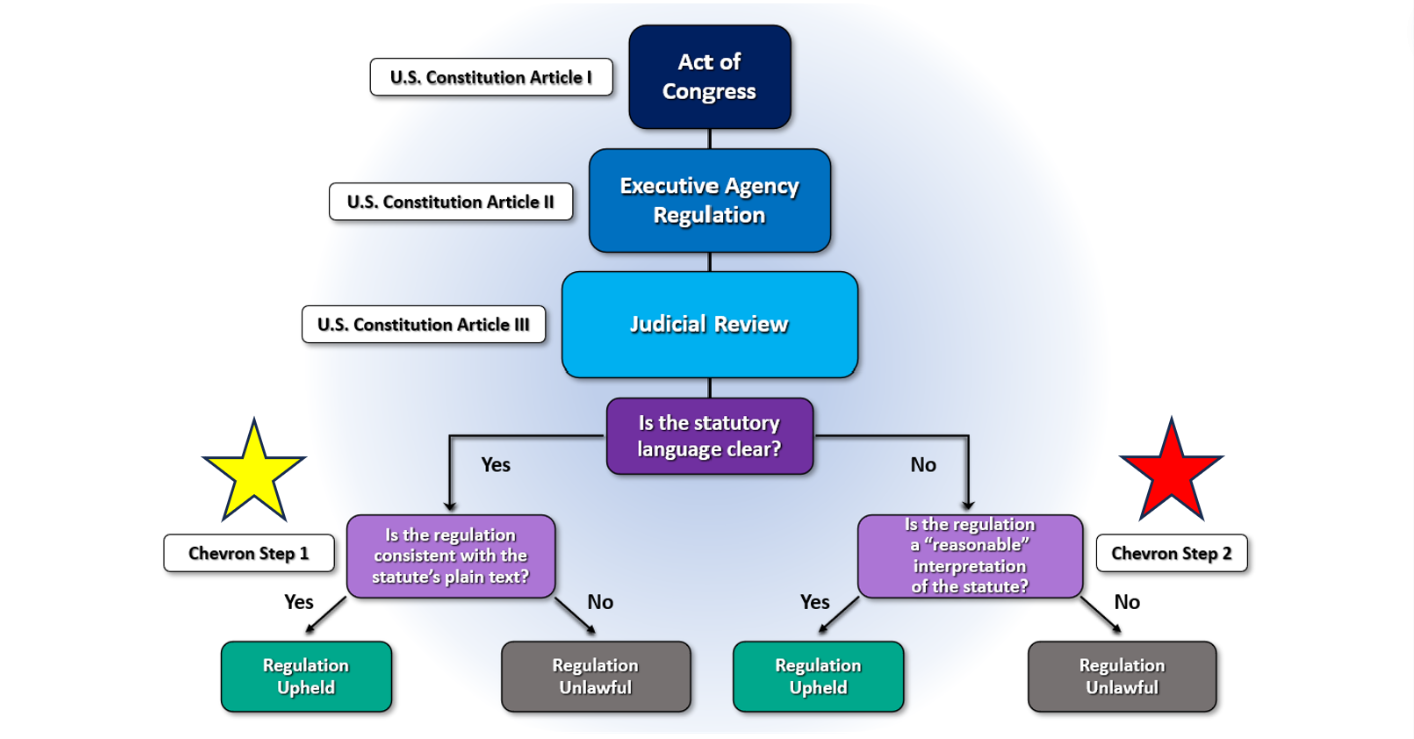
Chevron ruling explained – The Chevron ruling, formally known as Chevron U.S.A., Inc. v. Natural Resources Defense Council, Inc., is a landmark 1984 Supreme Court decision that established a two-step framework for courts to review agency interpretations of ambiguous statutes.
Chevron ruling explained is a doctrine that defers to an agency’s interpretation of its own regulations. In some cases, this deference can be overturned, as seen in the case of overturned chevron. Despite this possibility, chevron ruling explained remains an important principle that helps agencies interpret and enforce their regulations.
Prior to Chevron, courts used a variety of approaches to review agency interpretations, leading to inconsistent and unpredictable outcomes. The Chevron ruling sought to provide a more structured and deferential approach to judicial review, giving agencies greater leeway to interpret the statutes they administer.
Chevron ruling is a technique used to create a diagonal pattern on fabric. It is often used in tartan patterns , which are characterized by their criss-crossed lines. The chevron ruling technique can also be used to create other patterns, such as stripes and zigzags.
Chevron ruling is a relatively simple technique to learn, and it can be used to create a variety of beautiful and unique fabrics.
Two-Step Process
The Chevron ruling established a two-step process for courts to review agency interpretations of ambiguous statutes:
- Step 1: Determine if the statute is ambiguous. If the statute is clear and unambiguous, the court must apply the plain meaning of the statute and defer to the agency’s interpretation.
- Step 2: If the statute is ambiguous, determine if the agency’s interpretation is reasonable. The court must defer to the agency’s interpretation if it is reasonable and based on a permissible construction of the statute.
The Chevron ruling has been highly influential and has been applied in numerous subsequent cases. It has helped to streamline judicial review of agency interpretations and has given agencies greater flexibility to interpret the statutes they administer.
Impact on Regulatory Agencies

The Chevron ruling significantly impacted the authority of regulatory agencies, granting them greater deference in interpreting statutes they administer.
Under the ruling, courts are required to defer to agency interpretations of statutes when those interpretations are reasonable and supported by the statute’s text.
Limits and Exceptions to Agency Deference, Chevron ruling explained
Despite the general rule of deference, courts may not defer to agency interpretations that are:
- Arbitrary or capricious
- Inconsistent with the statute’s plain meaning
- Based on a clearly erroneous reading of the statute
Implications for Judicial Review: Chevron Ruling Explained

The Chevron ruling has significantly impacted judicial review of agency actions, altering the balance between judicial deference and independent review.
Under Chevron, courts are required to defer to an agency’s interpretation of a statute it administers if that interpretation is reasonable, even if the court would have reached a different conclusion. This deference stems from the recognition that agencies possess expertise in their respective fields and are best equipped to interpret the statutes they enforce.
Judicial Deference
- Courts must defer to an agency’s reasonable interpretation of a statute.
- This deference is based on the agency’s expertise and experience in administering the statute.
Independent Review
Despite the deference accorded to agencies, courts retain the authority to independently review agency actions to ensure they are not arbitrary, capricious, or an abuse of discretion.
This review involves examining the agency’s decision-making process, the evidence relied upon, and the reasonableness of its conclusions.
Tension Between Deference and Review
The Chevron ruling creates a tension between judicial deference and the need for independent review.
Deference ensures that agencies have the necessary flexibility to implement complex statutes, while independent review safeguards against arbitrary or unlawful agency actions.
Courts must carefully balance these competing interests, ensuring that agencies are given appropriate deference while also upholding the rule of law.
The Chevron ruling, explained, provides a framework for courts to defer to agencies’ interpretations of ambiguous statutes. This principle of deference is rooted in the concept of stare decisis , which holds that courts should follow established precedents to ensure consistency and predictability in the law.
By applying Chevron deference, courts can avoid second-guessing agencies’ expertise and promote efficient and consistent implementation of complex regulatory schemes.
Chevron ruling explained can also be applied to other geometric patterns like the tartan pattern , where the stripes run diagonally across the fabric. This technique creates a dynamic and visually appealing effect that can add depth and interest to any design.
Understanding chevron ruling explained can help you create beautiful and eye-catching patterns that can be used in a variety of applications.
Chevron ruling, a pattern of repeated V-shaped elements, finds its inspiration in the dynamic lines of a chevron. This motif echoes the intricate geometries found in tartan patterns , where intersecting lines create a kaleidoscope of colors and shapes. Chevron ruling, like tartan, exudes a timeless elegance, making it a versatile design element that transcends fashion and interiors.